Industry Challenges
As Florence Nightingale once observed, “The goal of nursing is to put the patient in the best condition…”
Today’s retention and recruitment landscape begs the question: What strategies can healthcare entities utilize to put nurses in the best condition to deliver quality care and to prevent exacerbation of existing staffing challenges?

For at least twenty years, steadily coalescing factors have posed a threat to the nursing profession that, if continued, may result in a critical RN staffing shortage. The ramifications of an insufficient nursing workforce would spread throughout the entire healthcare infrastructure.
Nurses don’t struggle or consider leaving their profession due to patient care; they struggle when tasked with excessive workloads and when administrative support proves inadequate. Healthcare entities can make efforts toward combating RN staffing challenges, such as providing equipment that aids delivery of more effective, more efficient care. Better equipment and care delivery options result in more manageable workloads and improved patient outcomes. Empowered nurses and comfortable patients inherently result in greater career fulfillment.
The Macy Catheter®
When the oral route is compromised and ineffectively mitigates symptoms near end-of-life, alternate methods for medication administration like sublingual (SL), intravenous (IV), subcutaneous (SubQ), and suppositories can ultimately be burdensome and costly.
IV, SubQ, and suppository alternatives must be ordered, delivered, and set up, processes that can encumber patients, families, and clinicians with symptom control delays that may span hours or even days. Symptom control delays yield higher transfer rates to in-patient units, which can be a costly, arduous process.
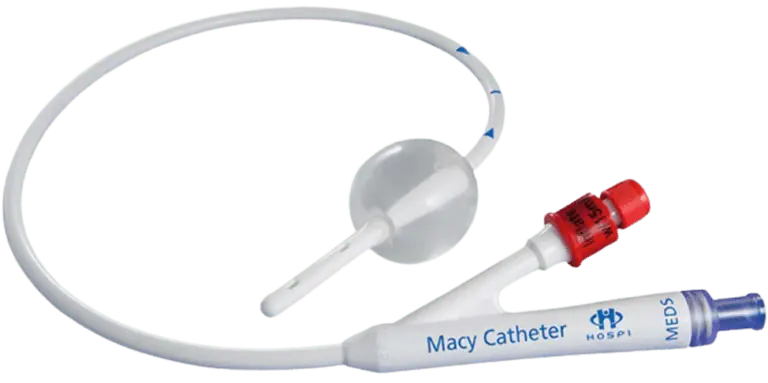
By equipping nursing staff with an easy method for rapid administration of medication and fluids, the Macy Catheter® can help nurses manage patients’ symptoms in a single, short visit. The device is the optimal alternative when oral delivery is compromised—particularly for hospice and palliative care cases—although the device is equally applicable to skilled nursing, emergency departments, and home healthcare settings.
Patented and FDA-cleared, the Macy Catheter® provides access to the clinically proven rectal route of delivery. It is designed to render the rectal route a practical, painless, and discreet alternative for medications that can be prescribed per rectum.
The Nursing Staffing Crisis
RNs represent a healthcare vanguard—the frontline’s frontline—and comprise the largest staffing group within the broader field, accounting for 40% of staffing operating costs.[1] However, roughly two decades of industrywide cost-cutting has heavily targeted nurses, resulting in significantly overburdened personnel.[2] The RN staffing shortage, while already concerning, is occurring at a time when an aging U.S. population has begun to place an increasing strain on healthcare infrastructure.
The United States Registered Nurse Workforce Report Card and Shortage Forecast projected a nationwide nurse shortage to emerge between 2016 and 2030.[3]

The nursing staffing shortage is becoming more and more pronounced in home health care (including SNF/ LTC, home care, and hospice), especially during the pandemic; COVID-19 upended schedules due to the new challenges of quarantine periods and exposures to the virus. The dire need for nurses in the hospital and/or acute care during the height of the pandemic created higher compensation offers.[5] Resultantly, many nurses have left home health care for higher paying positions in hospitals and other medical facilities.

Mitigation of nursing staffing shortages in home health care requires adoption of technology that empowers caregivers at home to partner with nurses throughout the ongoing care of the patient, resulting in more comfortable, higher quality care in the setting of the patient’s choice.

Looking to share this information?
Nursing Frustrations and Fatigue
Nurses’ work stress accumulates when their efforts to care for their patients require painful, invasive, or slow acting methods. When nurses confront an inability to improve patient experiences and outcomes, frustration and fatigue can ensue.

For at least twenty years, steadily coalescing factors have posed a threat to the nursing profession that, if continued, may result in a critical RN staffing shortage. The ramifications of an insufficient nursing workforce would spread throughout the entire healthcare infrastructure.
Nurses don’t struggle or consider leaving their profession due to patient care; they struggle when tasked with excessive workloads and when administrative support proves inadequate. Healthcare entities can make efforts toward combating RN staffing challenges, such as providing equipment that aids delivery of more effective, more efficient care. Better equipment and care delivery options result in more manageable workloads and improved patient outcomes. Empowered nurses and comfortable patients inherently result in greater career fulfillment.
Using the Macy Catheter® to Mitigate Challenges
The Macy Catheter® facilitates use of oral medications already in the home, allowing patients, caregivers, and clinicians to avoid the frustration, delays, and costs usually associated with switching routes of medication delivery.
Key Benefit: Easier Placement
The Macy Catheter’s non-sterile placement requires roughly three minutes and remains viable for up nto 28 days. Once inserted, a caregiver inflates a small, soft balloon with 15ml of tap water to secure the catheter in place. The catheter is removed or easily expelled with a bowel movement and, depending on agency policy, the same or new catheter may be reinserted after the bowel movement. The device is designed to be as minimally invasive as possible and as easy as possible for caregivers to use.
Key Benefit: Effective Delivery
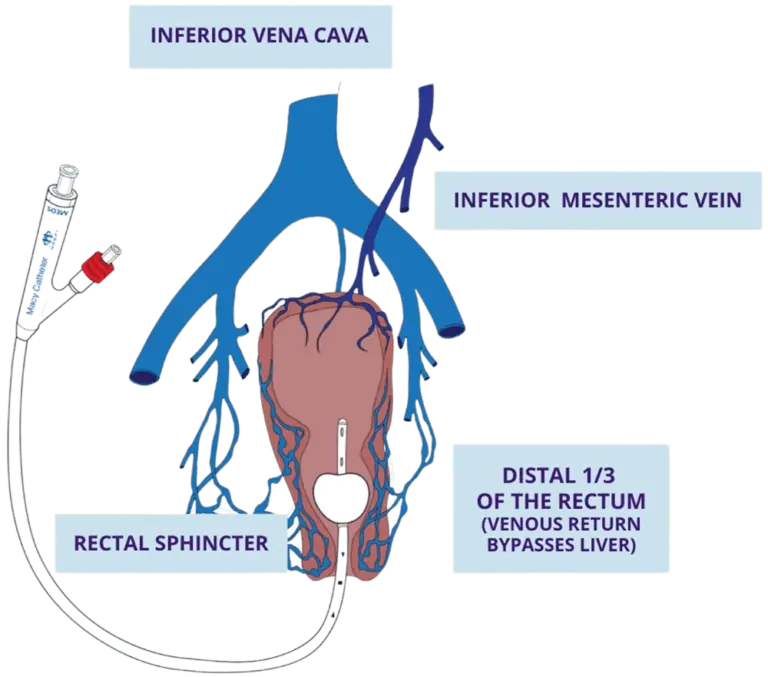
Use of the Macy Catheter® for medication administration is considered a “micro enema” (i.e., a volume under 20ml of rectally delivered medication best absorbed in the distal third of the rectum). Highly effective, micro enemas provide rapid care because:
- The rectal mucosa is highly vascularized.
- There is a high percentage of absorptive cells present.
- Liquid medications are absorbed and enter circulation quickly.
- Increased bioavailability (distal 1/3 of rectum venous return bypasses liver).
Key Benefit: Versatility
Most medications may be discreetly delivered via the single port placed on the patient’s leg. Caregivers may use Hospi’s LiquiPill to effortlessly grind tablet medication, add water, and create solutions (as directed by the prescriber).
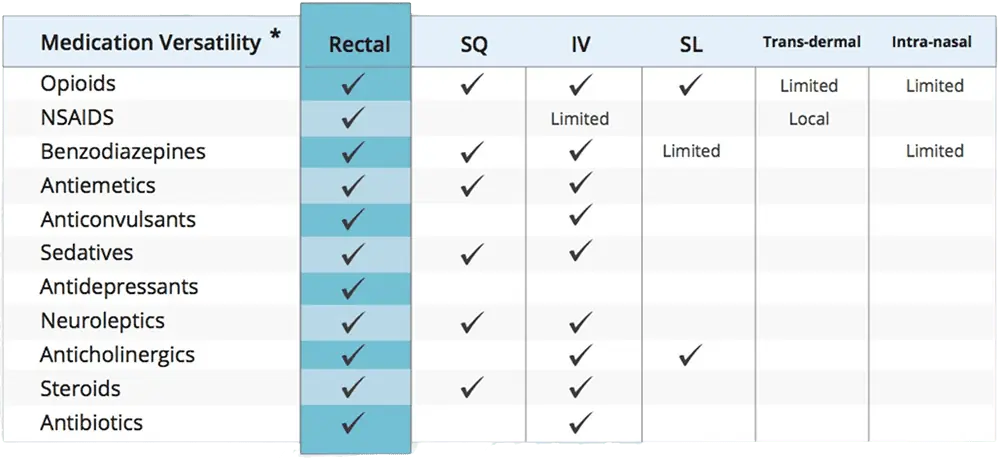
*Based on pharmacokinetic studies in literature.